
普段仕事で使っているRuby on Railsですが、ソースコードを読む機会もなかなかないので、試しにやってみることにしました
読めるようにするまで
以前書いた記事で読めるようにするまでの設定を画像キャプチャ付きで解説しましたので、よろしければこちらをご参照下さい
shitake4.hatenablog.com
読んだ箇所
2.11 JSON support
Active Supportが提供するto_jsonメソッドの実装は、通常json gemがRubyオブジェクトに対して提供しているto_jsonよりも優れています。その理由は、HashやOrderedHash、Process::Statusなどのクラスでは、正しいJSON表現を提供するために特別な処理が必要になるためです。
引用:RAILS GUIDES:Active Support コア拡張機能:JSON
※ to_json についてはこちらの記事を参照ください
ここからは上記記事の続きになります
ソースコードを読んでみる
as_jsonはどんな処理をしているのか見てみます
1. activesupport > lib > active_support > core_ext > object > json.rb
1. class Object
class Object def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: if respond_to?(:to_hash) to_hash.as_json(options) else instance_values.as_json(options) end end end
レシーバがrespond_to?(:to_hash) できる場合であれば、レシーバをハッシュにし、as_jsonしています
そうでなければ、 instance_valuesを呼んでいます
instance_variablesメソッドは、レシーバのオブジェクトが持っているインスタンス変数の名前を配列に入れて返します。
引用:Rubyリファレンス」instance_values
レシーバのインスタンス変数を持った配列に対して as_json しています
オブジェクトに対する as_json はハッシュか配列に変換して実行するということになります
2. class Hash
class Hash def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: # create a subset of the hash by applying :only or :except subset = if options if attrs = options[:only] slice(*Array(attrs)) elsif attrs = options[:except] except(*Array(attrs)) else self end else self end Hash[subset.map { |k, v| [k.to_s, options ? v.as_json(options.dup) : v.as_json] }] end end
subset = if options 省略 else self end
でoptionsが偽の場合はレシーバがsubsetに代入されます
真の場合は、if文内の最終評価値が、入ります
if options内をみてみます
if attrs = options[:only] slice(*Array(attrs)) elsif attrs = options[:except] except(*Array(attrs)) else self end
if attrs = options[:only]でattrsに代入し、attrsが真であれ場合 slice(*Array(attrs)) が実行されます
Hash.slice はactive support の拡張機能になります
Slice a hash to include only the given keys. Returns a hash containing the given keys.
{ a: 1, b: 2, c: 3, d: 4 }.slice(:a, :b) # => {:a=>1, :b=>2}This is useful for limiting an options hash to valid keys before passing to a method:
def search(criteria = {}) criteria.assert_valid_keys(:mass, :velocity, :time) end search(options.slice(:mass, :velocity, :time))If you have an array of keys you want to limit to, you should splat them:
valid_keys = [:mass, :velocity, :time] search(options.slice(*valid_keys))
レシーバから引数に指定した値と一致するキーを含んだハッシュを戻り値とします
*Array(attrs) で可変長引数として配列で初期化し、引数に渡しています
この部分の処理はオプション only で指定したキーのみをレシーバから取り出す処理になります
次に elsif attrs = options[:except] を見てみます
さきほどと似ている記述です
exceptもactive supoprtの拡張機能であり、sliceとは違い引数に指定した値をレシーバから除外し、ハッシュを戻り値とする処理です
Returns a hash that includes everything but the given keys.
hash = { a: true, b: false, c: nil} hash.except(:c) # => { a: true, b: false} hash # => { a: true, b: false, c: nil}This is useful for limiting a set of parameters to everything but a few known toggles:
@person.update(params[:person].except(:admin))
上記2パターンに当てはまらない場合は、レシーバが返ります
次に、こちらをみてみます
Hash[subset.map { |k, v| [k.to_s, options ? v.as_json(options.dup) : v.as_json] }]
処理を順番に見てみます
Hash[] はハッシュインスタンスの作成処理です
Hashクラスのクラスメソッドは、新しいハッシュ(Hashクラスのインスタンス)を返します。の中に[キー1, 値1, キー2, 値2, ...]のようにオブジェクトを並べると、それが新しいハッシュのキーと値になります。
[]内のオブジェクトの数が奇数のときは、例外ArgumentErrorが発生します。
引用:Rubyリファレンス:Hash
subset.map { |k, v| } はsubset(さきほどのif文内で戻り値ハッシュ) に対して map でkey, valueを取り出しています
続いて [k.to_s, options ? v.as_json(options.dup) : v.as_json] を見てみます
配列の先頭にkeyをto_sしたものをいれています
配列の2番目に三項演算子 options ? v.as_json(options.dup) : v.as_json の戻り値が入ります
つまり、ここでの処理はハッシュsubsetのキー、バリューそれぞれに対して as_json し、再度ハッシュ生成しています
3. class Array
class Array def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: map { |v| options ? v.as_json(options.dup) : v.as_json } end end
レシーバである配列の各要素に対してas_json しています
4. class Struct
class Struct #:nodoc: def as_json(options = nil) Hash[members.zip(values)].as_json(options) end end
ここまでHash[members.zip(values)]見てみます
まずHash[] はハッシュの初期化処理です
membersメソッドを調べてみると、
構造体のメンバの名前(文字列)の配列を返します。
Foo = Struct.new(:foo, :bar) p Foo.new.members # => ["foo", "bar"][注意] 本メソッドの記述は Struct の下位クラスのインスタンスに対して呼び 出す事を想定しています。Struct.new は Struct の下位クラスを作成する点に 注意してください。
zipメソッドを調べてみると
zipメソッドは、配列の要素を引数の配列other_arrayの要素と組み合わせ、配列の配列を作成して返します。transposeメソッドで[array, other_array, ...].transposeとしたときと同じく、行と列を入れ替えます。ただし、transposeメソッドと違って足りない要素はnilで埋められ、余分な要素は捨てられます。
arr1 = [1, 2, 3] arr2 = [4, 5] arr3 = [6, 7, 8, 9] p arr1.zip(arr2, arr3)[[1, 4, 6], [2, 5, 7], [3, nil, 8]]
valuesメソッドを調べてみると
構造体のメンバの値を配列にいれて返します。
例えば以下のようにして passwd のエントリを出力できます。require 'etc' print Etc.getpwuid.values.join(":"), "\n"
ここまでをまとめると、構造体からメンバー名とメンバーの値を取り出しハッシュへと変換しています
そしてそのハッシュに対し as_json しています
5. class TrueClass
class TrueClass def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: self end end
6. class FalseClass
class FalseClass def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: self end end
7. class NilClass
class NilClass def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: self end end
8. class String
class String def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: self end end
9. class Symbol
class Symbol def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: to_s end end
10. class Numeric
class Numeric def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: self end end
11. class Float
class Float # Encoding Infinity or NaN to JSON should return "null". The default returns # "Infinity" or "NaN" which are not valid JSON. def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: finite? ? self : nil end end
finite? を調べてみると
数値が ∞, -∞, あるいは NaN でない場合に true を返します。 そうでない場合に false を返します。
引用:Ruby2.5.0リファレンスマニュアル:finite?
数値として問題がない場合にレシーバを返すようです
12. class BigDecimal
class BigDecimal # A BigDecimal would be naturally represented as a JSON number. Most libraries, # however, parse non-integer JSON numbers directly as floats. Clients using # those libraries would get in general a wrong number and no way to recover # other than manually inspecting the string with the JSON code itself. # # That's why a JSON string is returned. The JSON literal is not numeric, but # if the other end knows by contract that the data is supposed to be a # BigDecimal, it still has the chance to post-process the string and get the # real value. def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: finite? ? to_s : nil end end
こちらは数値として問題ないか確認後文字列へ変換しています
13. class Regexp
def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: to_s end
レシーバをそのまま文字列へ変換しています
14. module Enumerable
def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: to_a.as_json(options) end
module Enumerable を調べてみると
繰り返しを行なうクラスのための Mix-in。このモジュールの メソッドは全て each を用いて定義されているので、インクルード するクラスには each が定義されていなければなりません。
引用:Ruby 2.5.0:Enumerable
mapやeach_with_indexなどがインスタンスメソッドとして定義されているクラスです
rubyでハッシュや配列を使う場合に、便利なメソッドが定義されています
to_a.as_json(options) ですので、レシーバを配列に変換し、as_json しています
15. class IO
class IO def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: to_s end end
レシーバをそのまま文字列へ変換しています
16. class Range
class Range def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: to_s end end
レシーバをそのまま文字列へ変換しています
17. class Time
class Time def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: if ActiveSupport::JSON::Encoding.use_standard_json_time_format xmlschema(ActiveSupport::JSON::Encoding.time_precision) else %(#{strftime("%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S")} #{formatted_offset(false)}) end end end
まず ActiveSupport::JSON::Encoding.use_standard_json_time_format を見てみます
module ActiveSupport 省略 module JSON 省略 module Encoding #:nodoc: class JSONGemEncoder #:nodoc: 省略 end class << self # If true, use ISO 8601 format for dates and times. Otherwise, fall back # to the Active Support legacy format. attr_accessor :use_standard_json_time_format 省略 # Sets the precision of encoded time values. # Defaults to 3 (equivalent to millisecond precision) attr_accessor :time_precision 省略 end self.use_standard_json_time_format = true 省略 self.time_precision = 3
アクセッサに use_standard_json_time_format が定義されており、デフォルトでtrueに設定されています
その為、 Timeクラスの as_json 内では基本的に xmlschema(ActiveSupport::JSON::Encoding.time_precision) が実行されそうです
ActiveSupport::JSON::Encoding.time_precision も同じようにアクセッサが用意されております
デフォルト値は3です
time_precisionを調べてみると
@y_yagi氏のrails commit log流し読み(2014/07/10)で仕様変更の経緯が解説されていました y-yagi.hatenablog.com
time_precisionはミリ秒の桁数のようです
ActiveSupport::JSON::Encoding.time_precision = 4に設定してみると
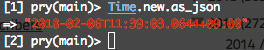
ミリ秒の桁数が4桁になりました
xmlschema を調べてみると
XML Scheme (date) による書式の文字列を返します。
引用:Ruby2.5.0リファレンス:Date#xmlschema
文字列を返すメソッドのようです
次に if ActiveSupport::JSON::Encoding.use_standard_json_time_format が偽の場合を見てみます
else %(#{strftime("%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S")} #{formatted_offset(false)}) end
まず%()を調べてみると
ダブルクオートで囲う場合と同等。
引用:Rubyで%記法(パーセント記法)を使う
ダブルクオートと同じようです
strftimeは引数のフォーマット文字列に従って、レシーバを変換し戻り値とします
時刻を format 文字列に従って文字列に変換した結果を返します。
引用:Ruby2.5.0リファレンス:Time#strftime
今回の引数の値の記号の意味はこちらになります
- %Y…西暦を表す数
- %m…月を表す数字(01-12)
- %d…日(01-31)
- %H…24時間制の時(00-23)
- %M…分(00-59)
- %S…秒(00-60) (60はうるう秒)
次にformatted_offset(false) を見てみます
active_support > core_ext > time > conversions.rb
class Time 省略 # Returns a formatted string of the offset from UTC, or an alternative # string if the time zone is already UTC. # # Time.local(2000).formatted_offset # => "-06:00" # Time.local(2000).formatted_offset(false) # => "-0600" def formatted_offset(colon = true, alternate_utc_string = nil) utc? && alternate_utc_string || ActiveSupport::TimeZone.seconds_to_utc_offset(utc_offset, colon) end
utc? && alternate_utc_string はUTCなのか、またはalternate_urc_stringを設定しているかを判定しています
設定している場合は戻り値が設定値になります
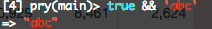
utc? && alternate_utc_string の判定が偽の場合を見てみます
ActiveSupport::TimeZone.seconds_to_utc_offset(utc_offset, colon) は世界標準時間からの差を出力します
※UTCについてはこちらの記事がわかりやすいかと思います
www.724685.com
18. class Date
class Date def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: if ActiveSupport::JSON::Encoding.use_standard_json_time_format strftime("%Y-%m-%d") else strftime("%Y/%m/%d") end end end
if ActiveSupport::JSON::Encoding.use_standard_json_time_format は 17. class Timeを参照してください
レシーバを文字列変換する処理をしています
strftimeは同様に 17. class Time を参照してください
19. class DateTime
class DateTime def as_json(options = nil) #:nodoc: if ActiveSupport::JSON::Encoding.use_standard_json_time_format xmlschema(ActiveSupport::JSON::Encoding.time_precision) else strftime("%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S %z") end end end
- class Timeと処理が似ています
use_standard_json_time_formatが真の場合は、time_precisionで指定した桁数でミリ秒で文字列へ変換し戻り値とします
偽の場合も同様に文字列に変換しています
20. class URI::Generic
class URI::Generic #:nodoc: def as_json(options = nil) to_s end end
21. class Pathname
class Pathname #:nodoc: def as_json(options = nil) to_s end end
22. class Process::Status
class Process::Status #:nodoc: def as_json(options = nil) { exitstatus: exitstatus, pid: pid } end end
Process::Status クラスがどのようなものか調べてみると
プロセスの終了ステータスを表すクラスです。 メソッド Process.#wait2 などの返り値として使われます。
引用:Ruby2.5.0:class Process::Status
exitstatus は
exited? が真の場合プロセスが返した終了ステータスの整数を、そ うでない場合は nil を返します。
引用:Ruby2.5.0:class Process::Status
pid は
終了したプロセスのプロセス ID を返します。
引用:Ruby2.5.0:class Process::Status
それぞれの値をハッシュにし戻り値としています
23. class Exception
class Exception def as_json(options = nil) to_s end end
読んでみて
JSON化するために様々なクラスをオープンクラスしていたので、Railsを使わずにJSONの処理をするときには気をつけないと思っていない挙動することがありそうだと思いました